Survival analysis
Predicting skin cancer risk from facial images with an explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) based approach. a proof-of-concept study
Check the online demonstration of this project here.
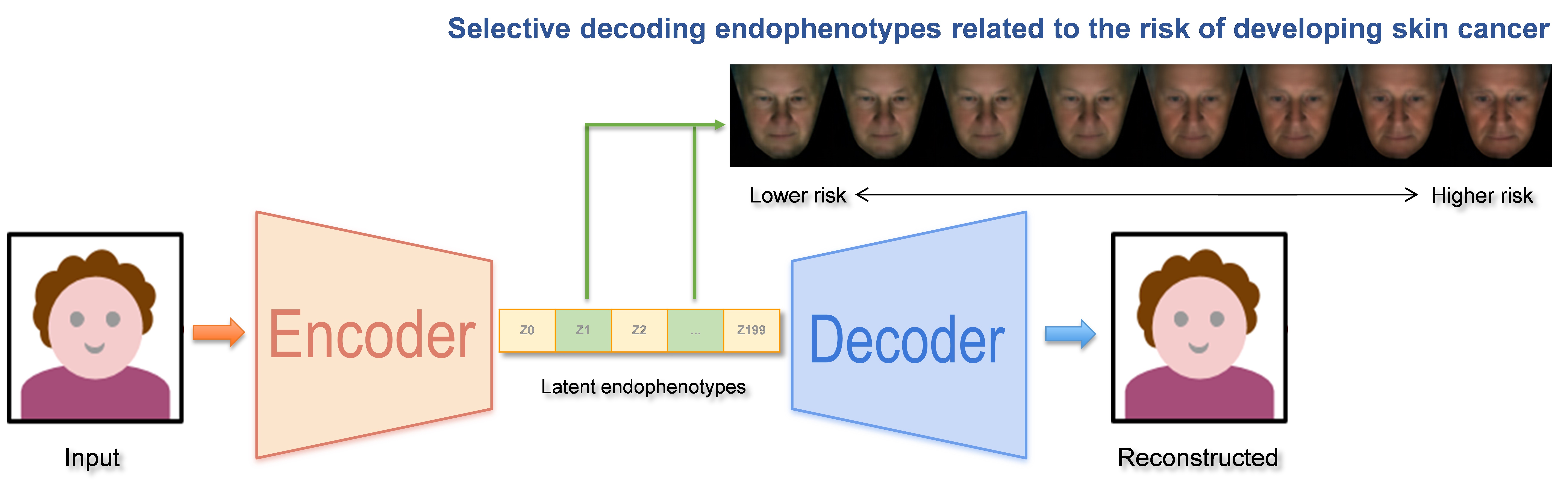
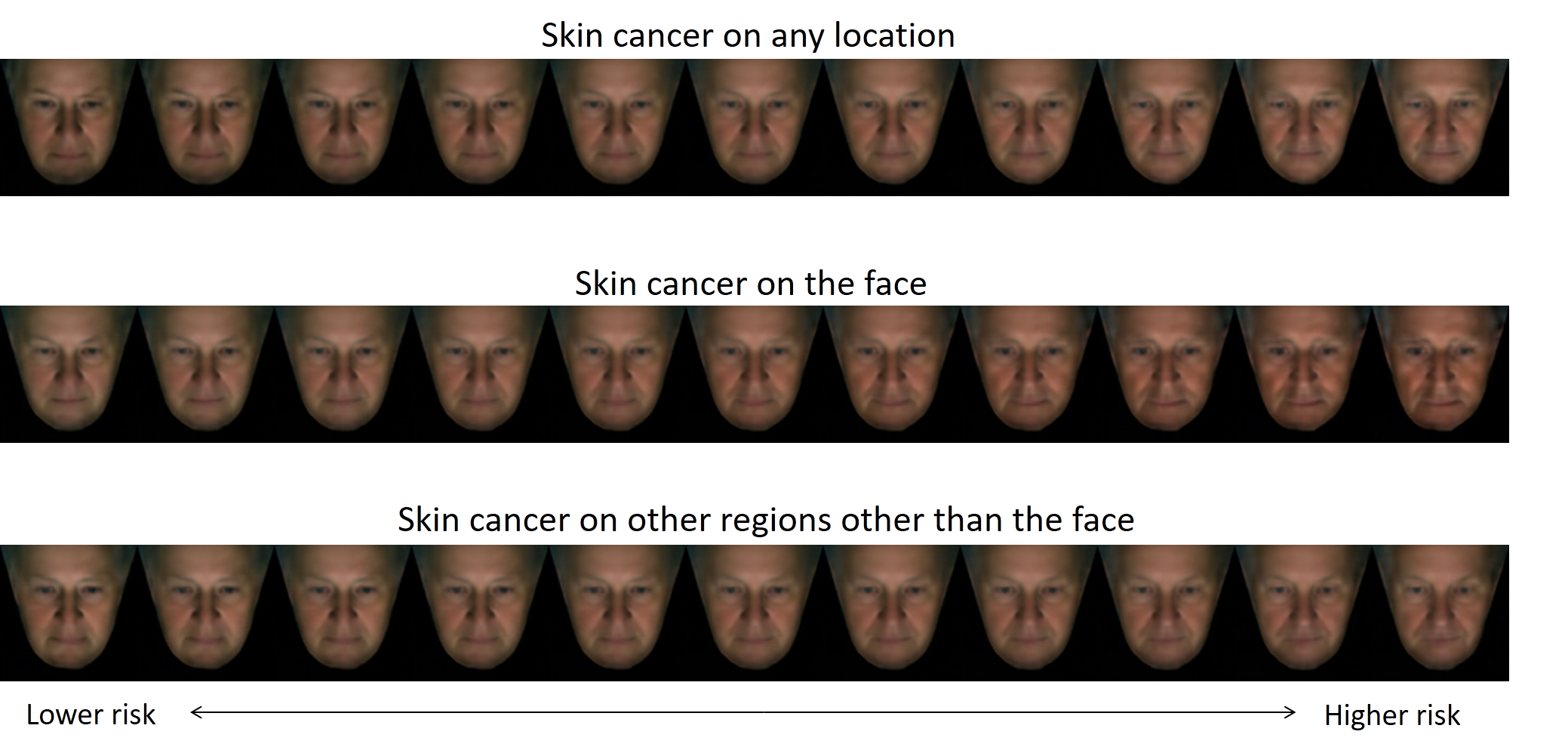
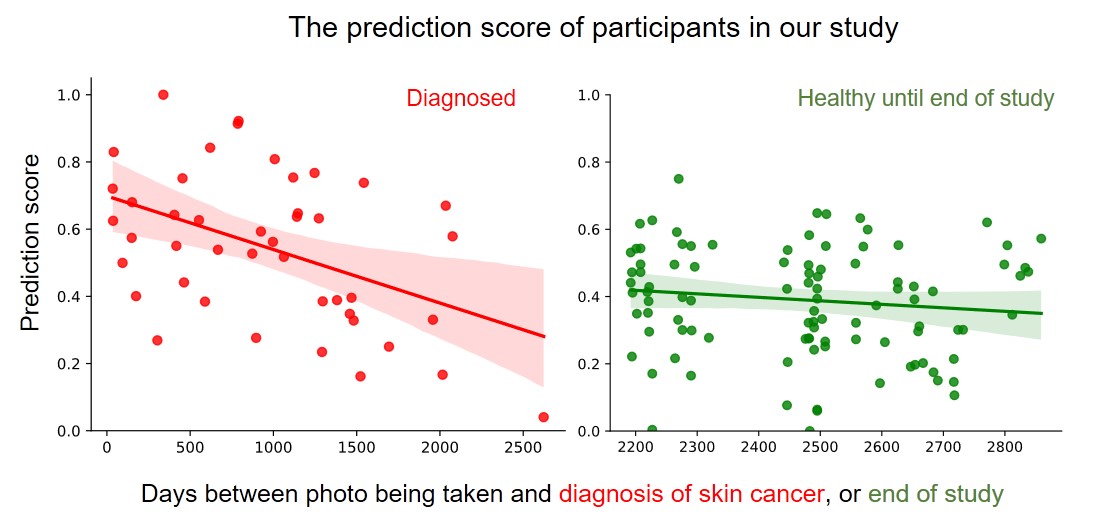
Efficient identification of individuals at high risk of skin cancer is crucial for implementing personalized screening. We present a neural network-based explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) approach for skin cancer risk prediction based on facial endophenotypes obtained from 2D facial images, and compare its efficacy to 18 established skin cancer risk factors using data from the Rotterdam Study. Among the 2,810 participants (mean Age=68.5 ± 9.3 years, average Follow-up=5.0 years), 228 participants were diagnosed with skin cancer at various body locations after photo acquisition. In the skin cancer survival analysis, our XAI approach achieved superior predictive accuracy based on facial endophenotypes (c-index=0.72, SD=0.05) for skin cancer diagnosis on any body location, outperforming that of the known risk factors (c-index=0.59, SD=0.03). Furthermore, our XAI techniques indicated facial features such as a lower BMI and increased facial erythema are linked with higher risk of developing skin cancer. This proof-of-concept study underscores the high potential of harnessing facial images and a tailored AI approach as an advanced predictive alternative over known risk factors for identifying individuals at high risk of developing skin cancer.
References
2024
- eclinmPredicting skin cancer risk from facial images with an explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) based approach. A proof-of-concept studyLancet’s eClinicalMedicine, 2024